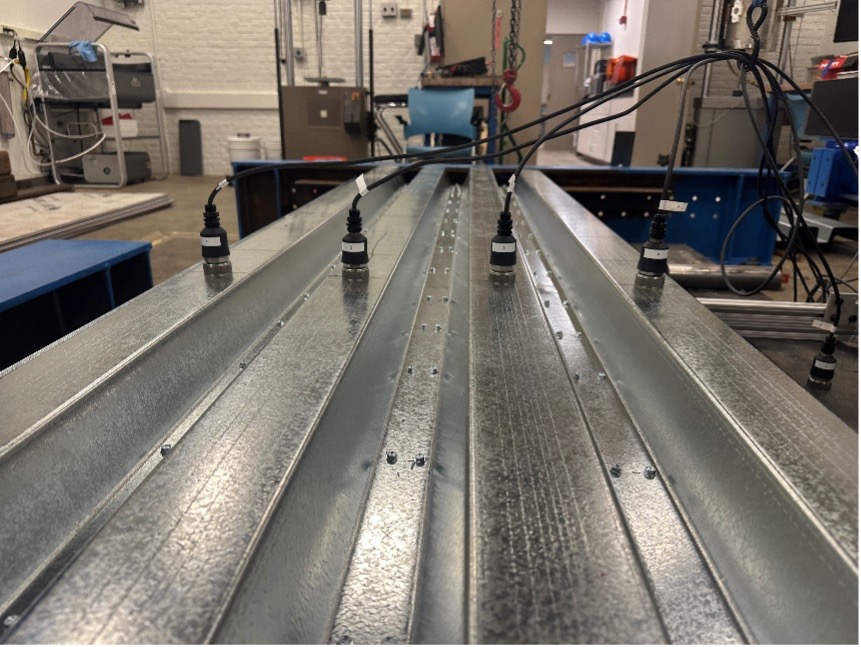
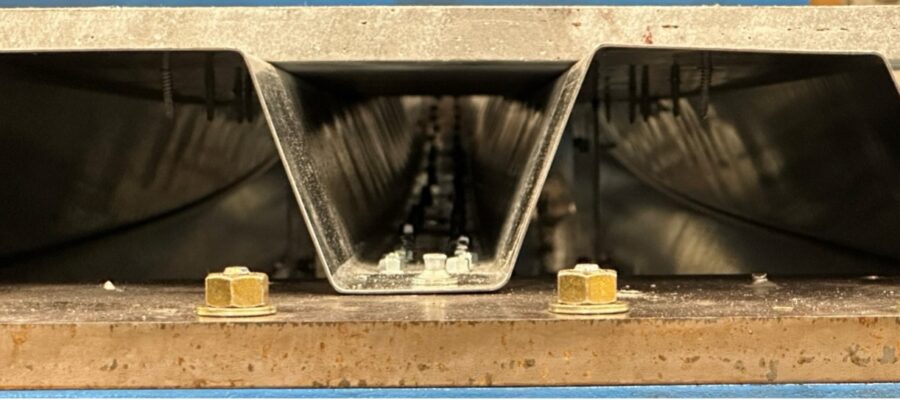
FastFloor-R is a robust, resilient, reliable novel composite steel floor system with strong applications in span lengths common to residential construction. The non-commercial prototype floor system consists of two 3-inch deep steel decks placed in opposing fashion to form an open cell, fastened to one another, and then topped with a cementitious panel (USG’s Structo-crete is utilized) fastened to the upper deck flanges. In addition, for vibration testing recently conducted a non-structural finish is added to the floor, including LVL adhered to the top of the cementitious panel and resilient channels and drywall attached to the bottom of the steel deck.
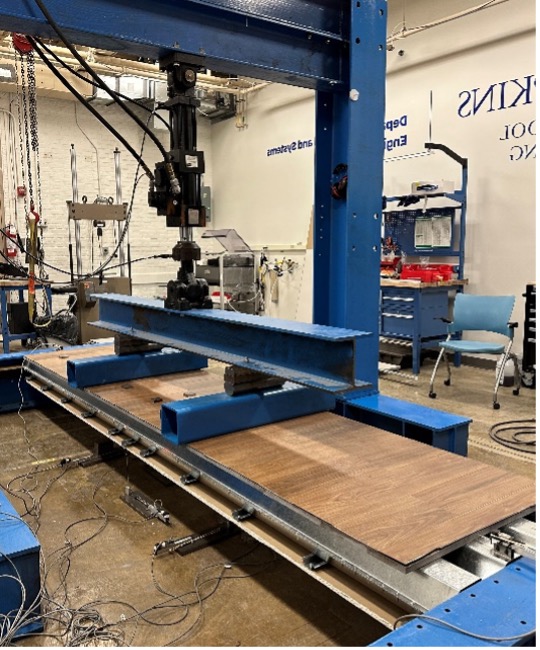

Two types of tests are conducted on each prototype: vibration, and structural. Tested specimens are 12 feet in length and 32 inches in width and are connected to supporting beams on shelf angles. Additionally, the research team will look at other floor assembly systems, including different end details for the supporting beams and using a “deep deck” (instead of two 3-inch decks) to construct a similar specimen.
Vibration tests are conducted after each step of assembly to understand how accelerations and frequency of the floor change with each additional component. Five accelerometers are utilized to measure the response and variety of vibrational inputs explored. The vibration tests include a bag drop, heel drop, impact hammer, and timed and untimed walking tests. These test results were measured from the specimen’s top and bottom of the specimen. The results of these tests will be compared to tolerances that are established in AISC Design Guide 11.